Securitization of Insurance Risk
Securitization of Insurance Risk
Securitization, a phenomenon well-known by the banking sector since the 1970s, has extended to the insurance sector for thirty years now. It has ever since continued to grow steadily with more experience in the non-life sector than in the life sector on which it has embarked recently.
A method for insurance companies to access capital and hedge risks by converting policies or underwriting risk into securities that can be sold in financial markets. Today, these complex techniques are accessible only to large insurance groups.
Therefore rather than an insurer transferring its underwriting risk to a reinsurer within the insurance industry, the risk is transferred to the broader capital markets.
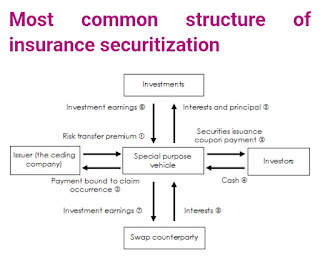
The general concept of insurance securitization, therefore, includes two elements:
-the transformation of liquidity generated by the underwriting into notes on the financial market.
-the transfer of the risks underwritten toward financial markets through notes trade.
A example of securitization is taking an illiquid asset or group of assets (policies or underwriting risk) and, through financial engineering, transforming it (or them) into a security.
The benefits of securitization in the insurance reinsurance industry is that by selling risks to investors, insurance companies reduce their need to hold capital and increase their ability to write new business. Securitization allows (re)insurers to focus on underwriting, structuring and passing risks directly to the debt capital markets, as well as improving their return on equity (ROE).
#benewinsurance #insurtech #inclusiveinsurance #insurance #reinsurance #takaful



Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for making this valuable comment.