Non-contributory Plan

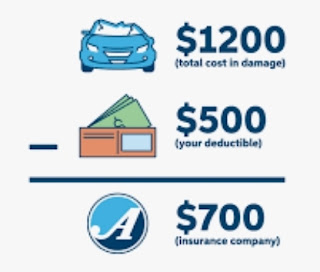
Non-contributory Plan A non-contributory plan is a type of benefit plan, such as a pension or retirement plan, in which the employer pays all of the contributions. Employees are not required to contribute financially to the plan. In these types of plans, the employer assumes the full cost of the employees' benefits. Non-contributory plans can be attractive to employees, as they receive these benefits at no direct cost to them. Employers might offer non-contributory plans to attract and retain talented employees Noncontributory plans are most beneficial for low-income employees, who might not otherwise be able to afford the associated benefits. Especially in group coverage plan. A non contributory Plan is applicable in; raditional pension plans, health insurance, disability insurance, life insurance. #benewinsurance #insurtech #inclusiveinsurance #insurance #reinsurance #takaful