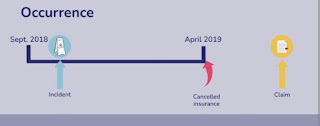
Risk Pooling
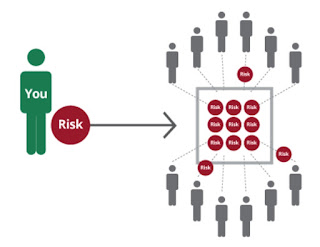
Risk Pooling Risk pooling simply means sharing the potential costs of risks among a large group of individuals or entities. By combining everyone's resources, the financial burden associated with any individual experiencing a loss becomes smaller and more manageable. This principle forms the foundation of all insurance models. There are basically two types of Risk Pooling: A. Formal insurance: Offered by companies, where individuals pay premiums and receive specific coverage in case of certain events. B. Informal risk-sharing arrangements: Groups like communities or families may create their own systems for mutual aid and support in times of need. When considering rusk pooling we understand individuals with a higher risk of making claims might be more likely to join the pool, which gives rise to the principle of moral hazard making the insurance more riskier. This is why a good mechanism must be put in place to ensure contribution and distribution of resources within the poo